Difference between revisions of "W-CDMA"
From SpenchWiki
(→Auto-correlation) |
|||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
Strong peaks precisely on the 10ms grid line are indicative of the pilot channel. | Strong peaks precisely on the 10ms grid line are indicative of the pilot channel. | ||
| − | There is also a smaller peak at ~0.7ms, which should be the repeating slot of the pilot channel. | + | There is also a smaller peak at ~0.7ms, which should be the repeating slot of the pilot channel (if you count the peaks correctly, the 14th 'harmonic' will land precisely on the first strong 10ms peak). |
* Telstra NextG at 842.5MHz: | * Telstra NextG at 842.5MHz: | ||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
[[File:NextG_FAC.png|800px]] | [[File:NextG_FAC.png|800px]] | ||
| − | Waterfall plot shows bursty traffic on the downlink | + | Waterfall plot shows bursty traffic on the downlink. |
Revision as of 21:11, 18 July 2011
Specs
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Modulation/Access scheme | W-CDMA |
| Channel bandwidth | 5MHz |
| Chip rate | 3.84MHz |
| Common pilot channel (CPICH) | Fixed-rate 30 Kbps, spreading factor (SF) 256 |
| Primary CPICH (CCPCH) | 14 slots in one radio frame |
| CCPCH slot | First 256 chips Tx OFF, then 18 data bits (20 bits/2560 chips in total) |
| CCPCH frame | 10ms total duration |
References
- A great PDF that deals with many technical aspects of the air interface.
Auto-correlation
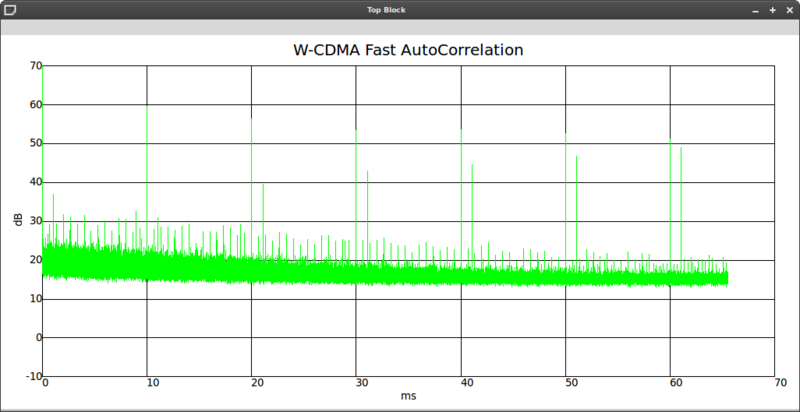
- 3G UMTS at 2.1125GHz:
Strong peaks precisely on the 10ms grid line are indicative of the pilot channel.
There is also a smaller peak at ~0.7ms, which should be the repeating slot of the pilot channel (if you count the peaks correctly, the 14th 'harmonic' will land precisely on the first strong 10ms peak).
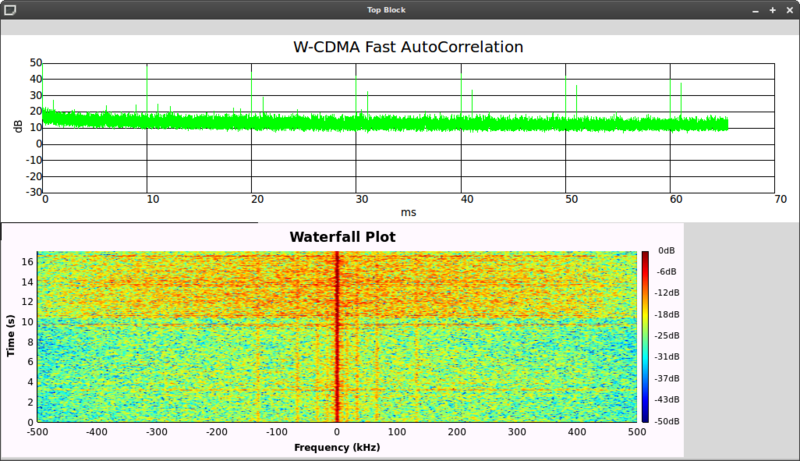
- Telstra NextG at 842.5MHz:
Waterfall plot shows bursty traffic on the downlink.